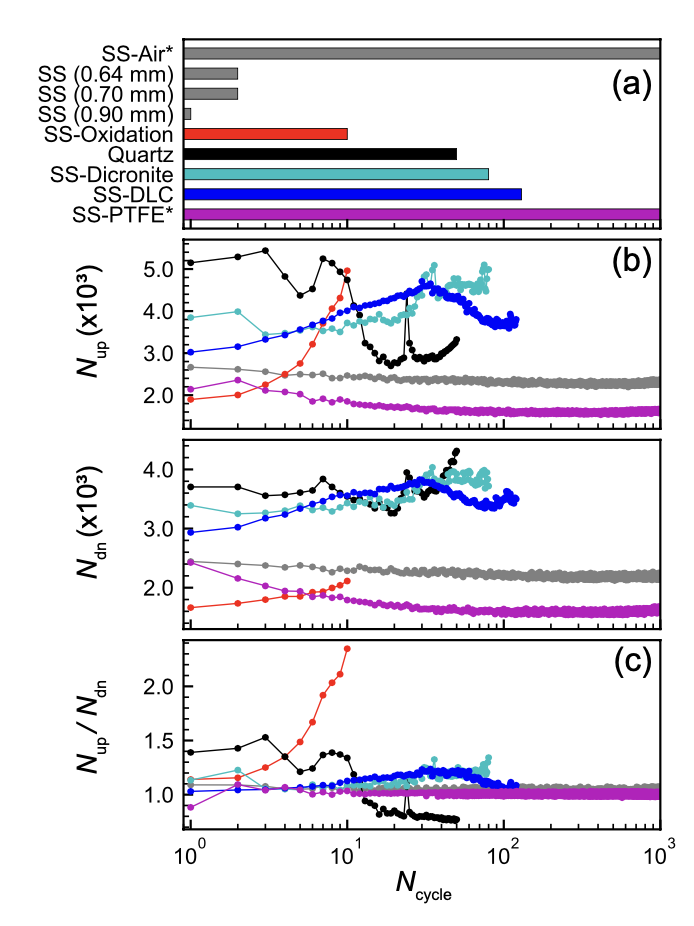
Systematic investigation of wear-induced cold welding in ultrahigh vacuum piezoelectric motors with non-metallic coatings
Piezoelectric motors are widely used in various applications where both precision positioning and miniaturization are required. Inertial or quasi-static motors are commonly employed because of their high accuracy, which demands consistent sliding friction between moving sliders and their static counterparts for reliable operation. In general, slider wear is unavoidable after long-term use. This wear can often lead to more serious cold welding in vacuum, which is also referred to as friction welding induced by direct contact between similar metal surfaces. Non-metallic coatings can prevent such unwanted cold welding in ultrahigh vacuum (UHV) applications. However, the practical reliability of available coatings under UHV conditions still remains to be elucidated. Here, we systematically investigate the practical reliability of commonly used, UHV-compatible lubricant coatings for piezoelectric motors in vacuum. We demonstrate that polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) shows the most reliable long-term operation in vacuum, while other coatings eventually lead to wear-induced cold welding and motor failure. Our findings provide a simple and effective method to improve the long-term performance of UHV piezoelectric motors by coating the slider surface with PTFE.